when acetyl-coa reacts with oxaloacetate to form citrate
Oxaloacetate is an intermediate of the citric acid cycle where it reacts with acetyl-CoA to form citrate catalyzed by citrate synthase. Oxaloacetate is also a potent inhibitor of complex II.
 |
| Chem 440 Citric Acid Cycle |
This attack is guided by the acetyl-CoAs hydrogen bond to the His274.
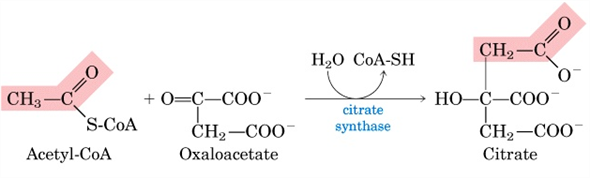
. In the second step of this reaction His320 protonates the carbonyl oxygen of oxaloacetate. This reaction is the entry point of two-carbon units into the citric acid cycle. In the first step of the citric acid cycle acetyl CoA reacts with oxaloacetate to form a Pyruvate b Citrate c NADH d ATP. He correct option among all the options that are given in the question is the third option or the penultimate option.
5 succinyl CoA is enzymatically converted to succinate. That citrate then goes through several steps to regenerate OAA. The reaction is subject to allosteric regulation. Acetyl-CoA H2O Oxaloacetate Citrate CoA.
If youre asking why you cant make oxaloacetate by running acetyl-CoA through the TCA cycle its because in the first step of the cycle acetyl-CoA reacts with OAA to form citrate. I hope that this is the answer that has actually come to. Oxaloacetate is the first substrate to bind to the enzyme. Question 10When acetyl-CoA reacts with oxaloacetate to form citrateAa new carbon-carbon bond is formedBan oxidative decarboxylation reaction takes placeCa dehydration reaction takes placeDa rearrangement takes placeEnone of theseBecause a new C-C bond is formed the condensation would normally be endergonic.
Acts as a base and abstracts a proton from acetyl-CoAs methyl group. Isoc-itrate is cleaved by isocitrate lyase into suc-cinate and glyoxylate. 6 succinate is oxidized to fumarate. This step forms a neutral enol.
4 alpha-ketoglutarate loses a molecule of carbon dioxide and is oxidized to form succinyl CoA. Only when this citryl-CoA has formed will another conformational change cause thioester hydrolysis and release coenzyme A. Once this occurs the enols 2-carbon can attack oxaloacetates carbonyl to produce citryl-CoA. Important difference is that two molecules of acetyl CoA enter per turn Citrate is then isomerized to isocitrate.
Mitochondrial citrate synthase dimer catalyzes the irreversible reaction of acetyl-CoA water and oxaloacetate to form citrate and coenzyme A. Biochem chapter 19 Study online at stores into glucose. It is also involved in gluconeogenesis the urea cycle the glyoxylate cycle amino acid synthesis and fatty acid synthesis. This induces the enzyme to change its conformation and creates a binding site for the acetyl-CoA.
At the start of the Krebs cycle acetyl CoA reacts with oxaloacetate molecule to form citrate a six-carbon molecule. 3 isocitrate loses a molecule of carbon dioxide and then undergoes oxidation to form alpha-ketoglutarate. This ensures that the energy released from the thioester bond cleavage will drive the condensation. Acetyl CoA condens-es with glyoxylate to form malate in a re-action catalyzed by malate synthase and then malate is oxidized to.
Then in a succession of reactions 2 citrate is rearranged to form isocitrate.
 |
| Chapter 16 Solutions Lehninger Principles Of Biochemistry 4th Edition Chegg Com |
 |
| 26 11 How Do Enzymes Work Citrate Synthase Chemistry Libretexts |
 |
| Nucleophilic Attack Of Enolate To Oxaloacetate Oaa In Citrate Download Scientific Diagram |
 |
| The Citric Acid Cycle Cellular Respiration Article Khan Academy |
 |
| Krebs Cycle Citric Acid Cycle Tca Cycle With Steps And Diagram |
Posting Komentar untuk "when acetyl-coa reacts with oxaloacetate to form citrate"